Whenever you browse online, you usually type the website's name starting with WWW. However, you may have noticed the HTTP or HTTPS abbreviation in the browser's address bar. The Hypertext Transfer Protocol was the primary online communication method for a long time. But the S part is what really makes contemporary online communication secure.
The S in HTTPS stands for Secure, which refers to the Secure Sockets Layer protocol. This protocol adds one of the strongest online privacy protection tools to your traffic: encryption. Instead of sending online traffic in plain text, which is highly susceptible to Man-in-the-middle attacks and other surveillance methods, SSL encryption guarantees data privacy.
It also lays the foundation for data integrity using the Transport Layer Security protocol, so you'll often hear SSL/TSL together. These two protocols combined encrypt your data and verify it using the message authentication codes to ensure it has not been tampered with. This has numerous benefits, but before we dive into SSL encryption use cases, let's briefly overview the encrypted online communication model.
How Does an SSL Connection Work?
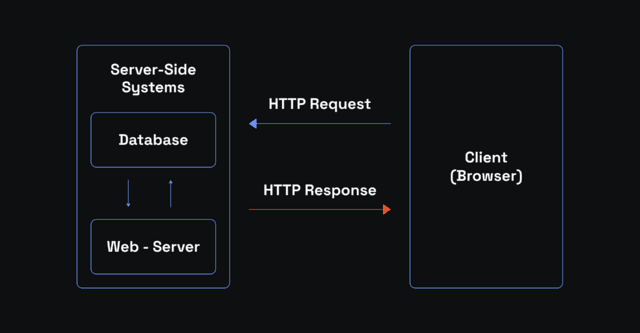
The standard online communication involves two main players: the client and the server. Whenever you browse online, your web browser sends requests to specific websites asking for data. The websites are stored on servers, and your browser is a client. The HTTPS or the (very rarely nowadays) HTTP protocols regulate the data exchange.
The SSL/TLS protocols do not change this flow but add essential extra layers, such as SSL certificates. It creates a secure and encrypted connection between your internal client (web browser, desktop and mobile apps, game clients, etc.) and the web server. Here's a brief rundown of how it works using the web browser as an example:
1. You type the website's address, and the browser sends the URL, headers, and HTTP method in an unencrypted form to the server.
2. The first response from the server sends back its SSL/TLS certificate that includes the domain name and other relevant website information, as well as the public cryptographic key.
3. Your browser verifies the received certificate, checking its validity period, domain matching, and certificate authenticity.
4. Upon successful verification, the client initiates a handshake with the server to create an encrypted tunnel.
5. The client then uses the public key sent with the certificate to create the Pre-Master Secret. This secret value is sent to the server encrypted.
6. The server uses its private key to decrypt incoming traffic to get the Pre-Master Secret.
7. Lastly, the server uses mathematical functions to derive a unique Session key for encrypting and decrypting client-server communication.
What a mouthful. However, this complex cryptographic key exchange, coupled with unique key derivation, ensures online communication privacy.
Firstly, cybercriminals cannot decrypt the traffic using current technology because contemporary encryption algorithms are nearly unbreakable by current computing power. Second, even if they manage to intercept the communication via MITM attacks, they cannot derive the unique session key forged using advanced mathematical functions, leaving hackers barehanded.
How Do SSL Proxies Work?
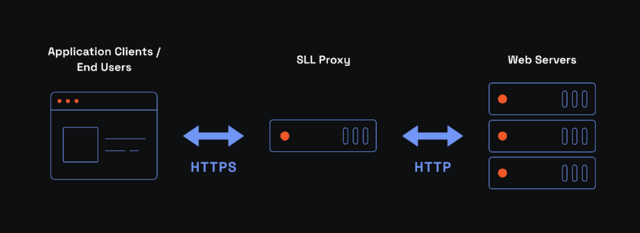
The method above is secure but not foolproof, and an SSL proxy fixes some of its shortcomings. By now, you probably know that a proxy server stands as an intermediary between your device and online servers. One of its many advantages is the obfuscation of the IP addresses.
In HTTP and HTTPS communication, the client always uses its original IP address unless it is channeled via a proxy server or a VPN. This creates more than a few significant problems. Firstly, IP tracking is one of the more popular online surveillance methods, so if you continuously expose your IP online, it's easier to get your data. This may not be a huge issue in democratic countries, but political activists living in an authoritarian regime can experience severe persecution.
Then there's censorship and geographical restrictions. Internet service providers can issue geographically determined IP restrictions, such as denying access to Facebook and BBC in Russia or Discord and YouTube in Iran, etc. Once again, a proxy bypasses censorship because it reroutes your traffic through an additional server located in a different location. So, if you connect to a proxy in the US from Russia, you can bypass geographical restrictions and maintain unrestricted internet access.
An SSL proxy is not that much different from a standard proxy server, but its encryption benefits are significant. Proxy SSL expands encryption scope and includes the gap between the client and a proxy server bypassing ISP surveillance. Typically, Internet service providers can collect some user data, depending on national laws.
For example, ISPs in the United States can legally gather and sell user data without their consent. An SSL proxy server reroutes your traffic from the ISP, protecting your online identity from unwanted attention.
Benefits Of Using an SSL Proxy
The SSL proxy benefits are not limited solely to online privacy or unrestricted Internet access. SSL proxies are particularly popular among business managers and play an important role in cybersecurity. Let's go over the essential SSL proxy benefits in more detail.
Corporate Network Security
Workplace networks often host hundreds of employees simultaneously. It's only natural for humans to make mistakes, and unaware employees can stumble upon virus-infected websites, click on a malicious link, or download an infected attachment.
Without an SSL proxy, the infection would directly reach the corporate network, possibly spreading through multiple computers. To prevent this, cybersecurity specialists modify SSL proxy settings to inspect incoming traffic for malicious elements and neutralize them before reaching genuine devices.
Information Access
The internet is divided into regions, and much information is inaccessible depending on your geographical location. For example, due to GDPR laws, many websites in the US are unavailable to European visitors. This creates a significant problem for businesses with global reach because it may restrict crucial business information, such as product prices, user reviews, holiday discounts, etc.
Business managers connect to an SSL proxy server in a different region to avoid these restrictions and gather business intelligence without boundaries.
Data Scraping
Suppose you've used an SSL proxy to access geo-blocked information, but there's just so much of it. Going over commodity prices, user reviews, or social media posts manually is time-consuming and prone to human error.
That's where scraping comes in. You can combine your web scraper with SSL proxies to automate data-gathering tasks, simultaneously evading IP blocks whenever websites try to restrict information access.
Public Wi-Fi Security
After the emergence of smartphones, public Wi-Fi became much more widespread. Unfortunately, that also drew cybercriminals that exploit often insufficient Wi-Fi cybersecurity protocols to steal user data, like passwords or credit card numbers. Hackers launch MITM or Evil Twin attacks to lure unsuspecting users and steal their data.
Because SSL proxy creates a secure and encrypted tunnel between your device and online servers, all cybercriminals see is some gibberish and not your actual data.
Additional Benefits
SSL proxy is a versatile piece of software, so it can be used in many ways. For example, reverse SSL proxies can be tailored to inspect incoming traffic for malicious elements and also distribute online data flow between multiple SSL proxy servers to avoid server overload.
Tech-savvy users can customize proxy settings to deny access to specific websites, like social networks or online games at work, or torrenting and gambling sites at home with underaged children.
SSL Proxy vs VPN: Understanding the Difference
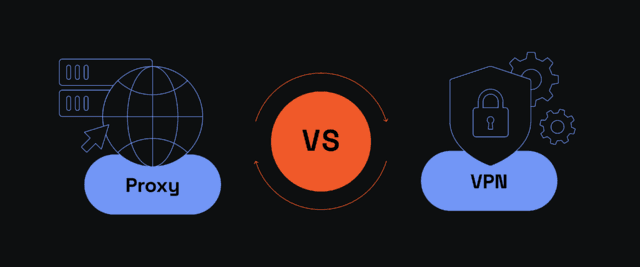
It is easy to mistake an SSL proxy for a VPN because both reroute your online traffic through a third-party server and encrypt it. By doing so, both technologies obfuscate the original user IP address and substitute it with an alternative. However, that's where similarities end. Here are the essential SSL proxy vs. VPN differences.
Encryption Scope
An SSL proxy typically encrypts only client-server communication without affecting the whole computer network. Meanwhile, VPNs encrypt all internet traffic, which has security benefits but also results in worse connection speeds for some apps.
Data Scraping
SSL proxy excels at data scraping because it offers a rotating residential IP feature that switches between high-trust score IPs to avoid website detection and bans. On the other hand, VPNs usually utilize only one server to protect your online privacy, but you'd have to switch manually to rotate IPs, which significantly slows down data scraping.
Customization
SSL proxies are highly customizable but require some tech know-how to adapt an SSL proxy to your particular needs. VPN apps are much more beginner-friendly but sacrifice customization options for user-friendliness.
Logging
Most consumer-centric VPNs follow strict no-logs policies and undergo independent audits to prove this because they are primarily an online privacy protection tool. Although some SSL proxies state the no-logs claim and are perfectly capable of hiding your online identity from unwanted attention, they rarely undergo audits to prove it. However, logging has specific benefits, such as working as a test ground for malware attacks in a secure and controlled environment.
Conclusion
The proxy SSL combination is a versatile and powerful tool with unique benefits for casual internet users and business managers simultaneously. But knowing its limits is best. SSL proxies excel at data scraping, geo-block evasion, and public Wi-Fi protection and can be used for traffic filtering or server load management.
They also protect your digital life from undesired attention but should be accompanied by additional cybersecurity tools that erase your browser fingerprint or spoof the GPS location on your mobile. However, considering the current state of online surveillance and user data mining, almost everyone can benefit from the additional SSL/TLS encryption.